It can get pretty confusing when you see terms like AI, machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks all used together these days. Each term has its own meaning, but they're often used to mean the same thing. This article is here to help you make sense of it all. We'll break down each concept, showing how they relate to one another while pointing out what makes them different.
Relationship Between the Terms
You can think of four concepts as being like the layers in a hierarchy. This structure shows how each concept builds on the last one, making the field of intelligent technology more complex and sophisticated.
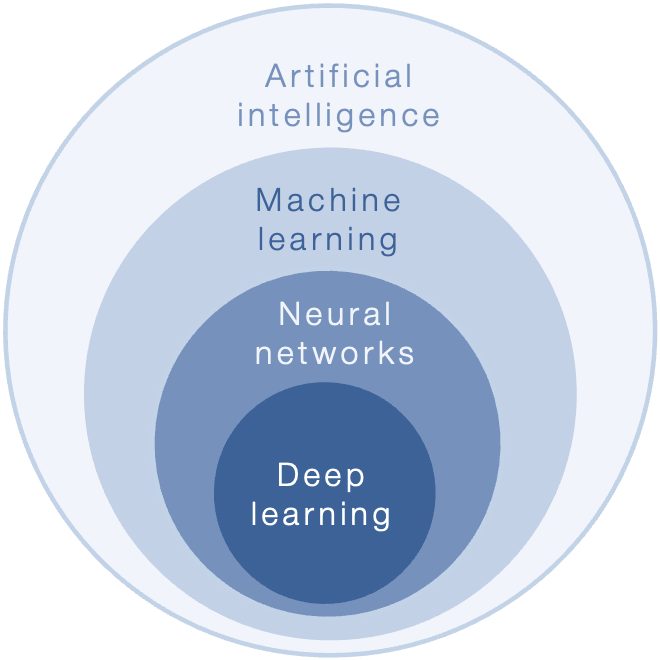
So, what sets deep learning and neural networks apart?
Think of a neural network as a simplified version of the human brain. It consists of interconnected nodes, called neurons, organized in layers. At its most basic, a neural network has three types of layers: an input layer that receives data, one or more hidden layers that process this data, and an output layer that delivers the results. This structure allows the network to learn patterns from the information it processes.
Now, let’s explore deep learning. It is like taking a neural network and adding extra layers — lots of them! When a neural network has multiple hidden layers, it becomes a deep learning model. These layers allow the system to understand complex patterns and make sense of intricate data. For instance, in image recognition, initial layers might identify simple features like edges, while deeper layers can recognize entire objects like faces or animals.
The main differences are:
1. Complexity
A basic neural network has just a few layers, making it simpler to train. Deep learning networks are more complex and can tackle challenging tasks.
2. Efficiency
Deep learning models handle large amounts of data efficiently. They learn from big data sets and give accurate results. Traditional neural networks may struggle with greater datasets.
3. Training time
Training a deep learning model takes time and resources because it needs a lot of data. Basic neural networks can be trained faster with smaller datasets.
4. Hardware needs
Deep learning systems use powerful hardware such as GPUs and lots of memory to perform complex calculations across multiple layers. Simple neural networks typically do not require as much computing power.
What's the difference between deep learning and machine learning?
Both are parts of AI, but they work differently. Machine learning involves algorithms that learn from data to make predictions or decisions. These algorithms often rely on human expertise to identify important features in the data, which means they can be limited by the knowledge of the designer. Techniques such as linear regression and decision trees are used in this area. They help ML work with smaller data sets.
Deep learning is an advanced form of machine learning that uses neural networks. These networks have multiple layers that help the model find patterns and features in large amounts of unstructured data, such as images or audio. Because it is self-sufficient, deep learning excels at complex tasks for example, image classification and speech recognition.
Basically, deep learning is a more sophisticated approach to machine learning that works well with complex and large data sets.
So, where does AI fit in here?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a fascinating field that enables machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as understanding language, solving problems, and making decisions. Think of AI as the brain behind technologies like voice assistants or chatbots that can interact with you in a natural way.
AI vs. Machine Learning
AI is a general term for technologies that copy human behavior. Machine learning is a specific type of AI that teaches computers to learn from data.
Simply put, machine learning allows computers to recognize patterns and make predictions based on past information without having to be explicitly programmed for each task. For example, when Spotify curates playlists based on your listening habits, that's machine learning at work, analyzing your preferences to suggest new songs you might enjoy.
- All machine learning is a form of AI, but not all AI relies on machine learning
AI vs. Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the creation of machines that can think and learn like humans. It includes everything from simple programs to advanced systems that can reason and understand language.
Artificial neural networks, on the other hand, are a specific type of AI inspired by how our brains work. Imagine a network of tiny "neurons" that connect and communicate to analyze data. These networks are excellent at recognizing patterns and making sense of complex information.
In essence, AI is the big picture of intelligent machines, while neural networks are the smart tools that focus on interpreting data.
AI vs. Deep Learning
Now, let's take a look at deep learning, a powerful branch of machine learning in AI. Think of deep learning as a layered approach to processing massive amounts of data. Each layer digs deeper and uncovers more insights — like peeling an onion.
What's exciting about deep learning is its ability to learn on its own. Unlike traditional methods that require human input to identify important features, deep learning models discover what matters automatically. This makes them fantastic for tasks like facial recognition and language understanding.
So while AI aims to create intelligent machines, deep learning uses layered networks to mimic human thinking in a highly effective way.
Deep Learning and Big Data
Deep learning has revolutionized the way we analyze large data sets, opening up new possibilities in a variety of fields. One of its outstanding features is its ability to improve accuracy as the amount of training data increases. While traditional machine learning models often hit a performance ceiling after processing a certain amount of data, deep learning models thrive on more information. This means that the more data you feed them, the better they get at recognizing patterns and making predictions.
Imagine trying to teach a child to recognize animals. If you show them just a few pictures, they might have trouble distinguishing a cat from a dog. But if you show them thousands of images, they start to notice subtle differences and can make much more accurate guesses.
Deep learning works in a similar way-its layered architecture allows it to learn from vast amounts of data, refining its understanding and increasing its predictive power. This capability is particularly valuable in areas such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous driving, where complex decisions depend on analyzing intricate data patterns.
FAQs
What’s the difference between artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad field that focuses on creating intelligent machines that can perform tasks that require human-like intelligence.
Within this field, machine learning (ML) is a technique that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed for each task.
Deep learning (DL) is a specialized type of machine learning that uses complex structures called neural networks — these networks have multiple layers that help them understand intricate patterns in data.
Is AI the same concept as neural networks?
AI is the generic field of intelligent systems, while neural networks are specific models designed to mimic how our brains work. Neural networks are essential components of many deep learning algorithms, but they don't represent the entirety of AI.
Are deep learning and AI similar things?
Deep learning is just one part of machine learning within the broader AI landscape. It focuses specifically on using layered neural networks to process data effectively and make predictions.
Machine learning vs. AI: what's the difference?
Machine learning is an important subset of AI that gives computers the ability to learn from massive amounts of data. Rather than relying on hard-coded rules for each task, machine learning algorithms identify patterns in data and apply those insights to make informed decisions.